
Our Office
Visit Us Online
-
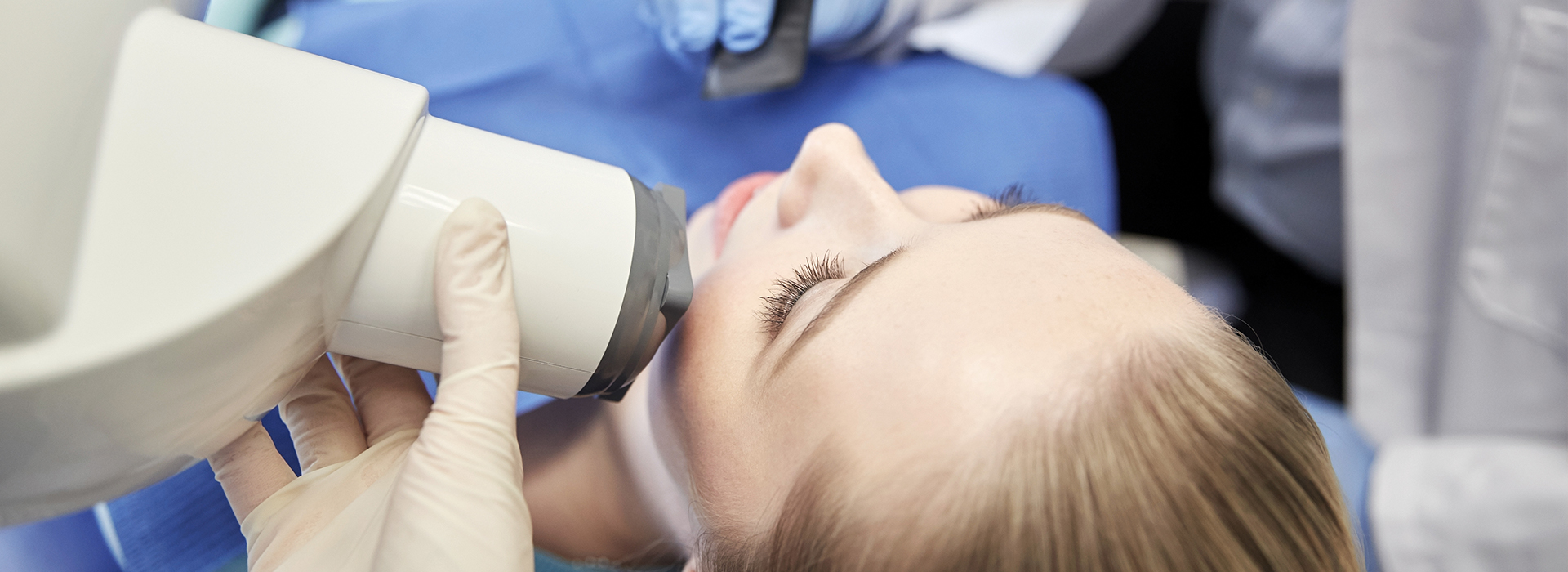
Digital radiography has transformed how dentists identify and plan treatment for oral health issues. High-resolution digital sensors capture detailed images of teeth, bone, and surrounding tissues, making it easier to spot cavities, bone loss, root fractures, and other conditions that may be invisible during a visual exam. These images can be enhanced on-screen—adjusting contrast, zoom, and sharpness—so clinicians can review subtle findings without repeatedly exposing a patient to radiation.
Because the images are available immediately, clinicians can compare current images with prior studies in real time. This side-by-side comparison helps in tracking disease progression or evaluating the success of previous treatments. The clarity and manipulability of digital images support more precise diagnoses and better-informed treatment recommendations, which leads to care that is tailored to each patient’s needs.
Patients benefit from a clearer explanation of their condition when clinicians use digital images during consultations. Being able to see the same high-quality images on a screen encourages understanding and informed decision-making. This transparency strengthens the patient-provider relationship and supports a collaborative approach to oral health planning.
One of the most noticeable advantages of digital radiography is speed. Unlike traditional film, which requires chemical processing and drying time, digital sensors transmit images to a computer almost instantly. That immediacy reduces chair time and eliminates delays between image capture and clinical interpretation, allowing appointments to run more smoothly and efficiently.
This efficiency is especially helpful during comprehensive exams, restorative appointments, or emergency visits where timely information is essential. Faster imaging means clinicians can make same-day decisions about diagnostics and interventions, minimizing the need for return visits solely to review radiographs. For busy families and individuals with limited time, that efficiency is a practical benefit.
Quick access to images also improves workflow among dental team members. Hygienists, assistants, and doctors can review the images concurrently and coordinate care without waiting for film processing. In short, digital radiography streamlines clinical operations while preserving the thoroughness of diagnostic evaluation.
Digital radiography significantly reduces patients’ exposure to ionizing radiation compared with conventional film-based x-rays. Modern sensors are more sensitive to x-ray photons, so they require a lower dose to produce diagnostic-quality images. This reduced exposure is an important consideration, particularly for children, pregnant patients, and individuals who require frequent monitoring.
Beyond the immediate dose reduction, many digital systems incorporate software features that optimize exposure parameters for each type of image. These safeguards help ensure that clinicians use the minimum radiation necessary to obtain a clinically useful image. The net result is a safer imaging environment without compromising diagnostic value.
While no imaging modality is entirely without risk, the adoption of digital radiography represents a meaningful step toward safer dental care. Clinicians balance the benefits of accurate diagnostics with conservative exposure practices to protect patient health over the long term.
Digital radiographs are stored electronically within patient records, eliminating the need for physical film files and chemical storage. Electronic storage simplifies long-term record keeping, reduces clutter, and makes it straightforward to retrieve past images when monitoring changes over time. Images can be archived in formats that integrate with practice management systems for reliable access during follow-up care.
Another practical advantage is the ability to share images quickly and securely with other healthcare providers when consultation or referral is needed. Whether consulting an oral surgeon, endodontist, or medical specialist, clinicians can transmit images electronically so colleagues can review the same high-quality data. This faster collaboration supports coordinated care and clearer communication between providers.
Because digital images are nondegradable and easily duplicated, they also safeguard continuity of care when patients change providers or relocate. The accessibility and permanence of digital records help ensure that future dentists have the diagnostic history necessary to make informed treatment decisions.
Dental x-ray procedures using digital radiography are familiar and straightforward. During the appointment, a small sensor is placed inside the mouth or positioned externally depending on the image required. The sensor connects to a computer, and within seconds—often while the patient is seated—the clinician can view the image. The process is quick, generally comfortable, and similar in positioning to traditional film x-rays.
Patients might notice the image appear instantly on a nearby monitor, which the clinician can then use to explain findings and next steps. For many, this immediate visual feedback is reassuring and helps clarify why a particular treatment is recommended. When appropriate, the radiographs are saved to the patient’s electronic record for future reference.
Safety protocols remain a priority: clinicians follow established guidelines for shielding and positioning, and exposure settings are tailored to minimize dose. If a patient has concerns—such as pregnancy or heightened sensitivity—staff will review options and determine the safest approach for capturing necessary diagnostic images.
At Morrison Dental Care, we use digital radiography to provide faster, safer, and more collaborative dental care for patients in Clifton Park and the surrounding communities. By combining advanced imaging technology with careful clinical judgment, our team aims to deliver precise diagnoses and treatment plans that support long-term oral health.
To learn more about digital x-rays or how we use imaging to support your care, please contact us for additional information. We’re happy to answer your questions and explain how digital radiography fits into a comprehensive approach to dental health.
Digital radiography is the use of electronic sensors and computer software to capture, display, and store dental X-ray images. Instead of traditional film, a small digital sensor records the X-ray exposure and converts it to a high-resolution image that appears on a monitor within seconds. These images can be enhanced, measured, and archived as part of the patient record for future reference.
Digital radiography includes intraoral images for tooth-level detail and extraoral images for broader views of the jaws and surrounding structures. The digital workflow eliminates chemical processing and paper film, making the process more efficient and environmentally friendly. Because images are stored electronically, they can be reviewed with patients and shared with specialists when coordinated care is needed.
When an X-ray exposure is made, a digital sensor placed inside or outside the mouth detects the X-ray photons and converts them into an electronic signal. That signal is sent to a computer where specialized software reconstructs and displays a diagnostic image almost instantly. Clinicians can then adjust contrast, zoom, and annotate the image to aid diagnosis and treatment planning.
There are different types of digital sensors, including direct sensors that connect to the computer and indirect plates that are scanned after exposure, as well as three-dimensional cone beam imaging for complex cases. The overall digital process streamlines image acquisition and integrates images directly into the patient’s electronic chart. This integration supports efficient documentation and collaboration across the dental team.
Digital radiography typically requires substantially less radiation than conventional film X-rays because the sensors are more sensitive and the imaging systems are more efficient. Protective measures such as lead aprons, thyroid collars, and properly collimated beams are used routinely to minimize exposure for every patient. Dentists follow professional guidelines to limit radiographs to the type and frequency appropriate for each patient’s clinical needs.
Certain populations, such as pregnant patients or very young children, may prompt additional precautions or modification of imaging protocols. Patients should always inform the dental team about pregnancy, recent medical imaging, or other health concerns so providers can tailor imaging decisions. When imaging is necessary, the combination of modern digital techniques and protective practices makes dental radiography a low-risk, highly useful diagnostic tool.
One of the primary advantages of digital radiography is reduced radiation exposure for the patient, while still delivering high-quality diagnostic images. Images are available immediately, which speeds diagnosis and allows the clinician to show and explain findings to the patient during the same visit. Digital images can also be enhanced with software tools to improve visualization of subtle problems that might be harder to see on film.
Additional benefits include easy storage and retrieval within the electronic patient record, the ability to share images securely with other providers, and elimination of chemical processing and film waste. These efficiencies support faster treatment planning and more coordinated care. Overall, digital radiography improves clinical workflow, patient education, and environmental sustainability.
After acquisition, digital radiographs are saved directly to the patient’s electronic record in the practice management or imaging software used by the office. These systems are designed to meet applicable privacy and security standards and allow controlled access by authorized clinical staff. Images can be retrieved instantly for follow-up visits, comparisons over time, or review during treatment planning.
When images need to be shared with specialists, laboratories, or referring providers, they are transmitted using secure methods to protect patient privacy. Digital files can be exported in standard formats for continuity of care while maintaining proper access controls. Secure storage and controlled sharing help ensure that radiographic information is available when needed without compromising confidentiality.
Yes, digital radiographs are a fundamental diagnostic tool for identifying dental caries, bone loss, root infections, and defects in restorations that are not always visible during a clinical exam. Bitewing images are particularly useful for detecting interproximal decay between teeth, while periapical images assess the roots and surrounding bone for signs of infection or pathology. The ability to adjust contrast and magnification can make early lesions easier to spot.
However, radiographs represent only one component of diagnosis and are used in conjunction with a clinical examination and patient history. Some early decay or soft-tissue issues may not show on X-rays, so the dentist will interpret images alongside visual inspection, periodontal assessment, and other diagnostic tests. Regular imaging at appropriate intervals helps detect problems early and guide timely treatment.
One of the strengths of digital radiography is speed: images appear on the computer screen within seconds of exposure, allowing immediate review by the clinician. Because of the rapid turnaround, dentists can discuss findings with patients and incorporate imaging results into the same appointment’s diagnosis and treatment planning. This efficiency reduces the need for return visits solely to review film results.
The time required for interpretation depends on the complexity of the case; routine images are assessed quickly during the exam, while more complex or comprehensive imaging may require additional review and consultation. If specialists are involved, images can be shared electronically for collaborative interpretation, which helps streamline decision-making without unnecessary delays.
Digital two-dimensional radiographs are commonly used for initial assessment and monitoring of many dental treatments, while three-dimensional cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) provides volumetric imaging for advanced planning. CBCT offers detailed views of bone volume, nerve locations, and anatomical structures that are essential for precise implant placement and complex oral surgery planning. Combining 2D and 3D imaging enables a comprehensive evaluation tailored to the procedure.
Digital imaging also integrates with other digital workflows such as CAD/CAM restorations and digital impressions, improving accuracy and predictability for restorative and surgical care. By using digital radiography alongside other modern technologies, clinicians can create more precise treatment plans and communicate expected outcomes more clearly to patients and collaborating providers.
Children benefit from digital radiography because sensors and exposure settings can be adjusted to the child’s size, reducing radiation dose while still obtaining diagnostic images. Dentists follow pediatric imaging guidelines to limit exposures to those necessary for diagnosis and treatment, using lead aprons and thyroid protection when appropriate. Clear communication with parents about the purpose and safety of radiographs helps ensure informed care for young patients.
For pregnant patients, elective radiographic procedures are typically deferred when possible, especially during the first trimester, unless the imaging is essential for urgent diagnosis or treatment. When radiographs are required, modern digital systems combined with shielding and careful technique keep doses very low. Patients should always inform the dental team of pregnancy so the dentist can apply appropriate precautions and determine the optimal timing for imaging.
Morrison Dental Care integrates digital radiography into routine exams and treatment workflows to provide fast, accurate diagnostic information and to enhance patient education. The team uses high-resolution images to detect cavities, assess bone health, and evaluate treatment outcomes while showing patients clear visuals to explain findings and options. Storing images in the electronic record allows for reliable comparisons over time and supports coordinated care when referrals are needed.
By pairing digital radiography with other advanced technologies and evidence-based protocols, Morrison Dental Care aims to make diagnostic processes more efficient and less invasive for patients. The practice emphasizes safety, clear communication, and careful image interpretation to support individualized treatment planning and long-term oral health.
Address:
1524 Route 9, Clifton Park, NY 12065